OVERVIEW KAZAKHSTAN
COUNTRY PROFILE
Kazakhstan
Explore the overview for a general context of how vulnerable and resilient Kazakhstan is to climate change. Explore climate impact and vulnerability by sector. View the results of the Climate Risk and Vulnerability Assessment for Kazakhstan. Explore the various options for climate adaptation in key sectors.
Country Context
The Republic of Kazakhstan is situated in north-central Eurasia. Kazakhstan’s terrain is diverse, with the country situated in four climate zones: forest-steppe; steppe; semi-desert and desert. Kazakhstan has a land area equal to that of Western Europe but one of the lowest population densities globally. According to an assessment, nearly 75% of the country’s territory is subject to high-risk ecological destabilization. The main source of economic growth is the country’s raw resources. Since 1985, Kazakhstan’s production of hydrocarbons has increased 225%. The country’s 2005 oil production amounted to 61.9 million tons and the production of natural gas was 25.2 billion cubic meters. Kazakhstan’s gross domestic product growth is accompanied by significant greenhouse gas emissions. It is estimated that around 75% of the country is at increased risk of adverse environmental impact to climate change.
Key Facts & Figures
Geography and population
With a territory of 2,724,000 km2, Kazakhstan is the largest country in the sub-region. Kazakhstan’s population of 18.8 million has a relatively low density of 6.9/km2, with 8.3 million (44%) living in rural areas and an urban population of 10.5 million (56%).
Economy
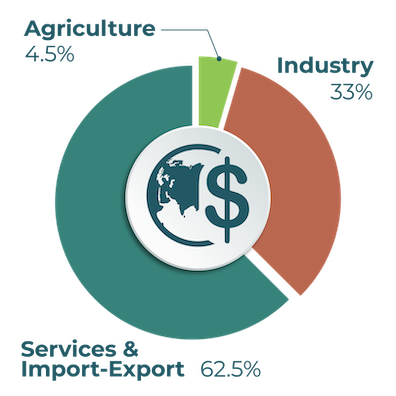
As Central Asia’s largest economy, Kazakhstan holds vast natural resources. Most of the economy is devoted to the services and import-export sector. Agriculture comprises a relatively small portion of the economy (4.5%).
Agriculture
The agriculture sector is dominated by wheat production, a major export crop. Other important crops include barley, cotton, sugar beets, sunflower and flax.
Land Use
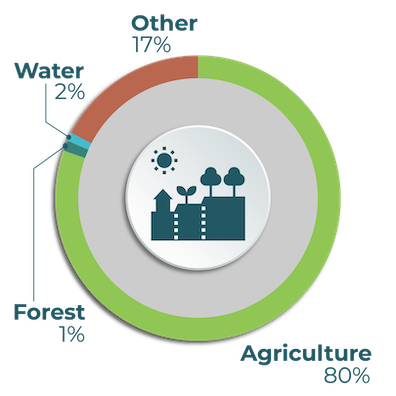
Kazakhstan utilizes most of its land for agricultural activities, which account for 5 per cent of GDP and employs a quarter of the population. Kazakhstan is the largest producer and exporter of wheat in the Central Asia region, which plays a central role in food security.
Energy Supply
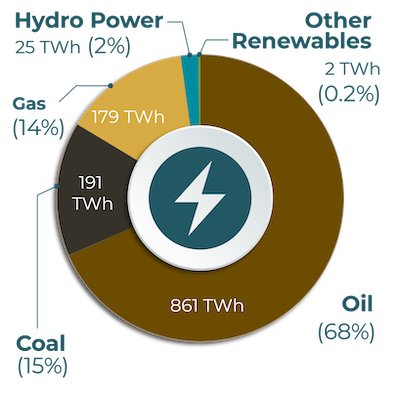
Kazakhstan derives most of its energy supply from non-renewable fossil fuel resources, including oil (68%), coal (15%) and gas (14%). The renewable resources supply makes up less than 3%, including 2% from hydropower.